Understanding how many countries are there in the world seems like a simple question, yet the answer is more complex than most people expect. The total number depends on definitions, political recognition, and international agreements. From fully independent nations to partially recognized states, the global map reflects centuries of history, diplomacy, and change. This article explains the numbers clearly, explores why confusion exists, and helps you understand how the world is officially organized today.
The Commonly Accepted Answer
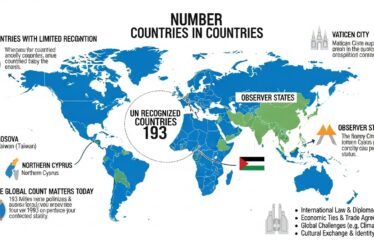
When people ask how many countries are there in the world, the most widely accepted answer is 195. This number includes 193 member states of the United Nations and two non-member observer states: Vatican City and Palestine. These entities meet the general criteria of having a defined territory, a permanent population, a functioning government, and the ability to engage in international relations.
The United Nations plays a central role in shaping the standard response to how many countries are there in the world. While UN membership is not the only measure of statehood, it provides the most practical and globally recognized benchmark.
Why the Number Is Not Universally Agreed Upon
Despite the popularity of the 195 figure, disagreement still exists. Some regions operate as independent countries in practice but lack full international recognition. This is why different sources may give different answers to how many countries are there in the world.
Territories such as Taiwan, Kosovo, and Western Sahara complicate the count. They have their own governments and borders but face political disputes that affect their recognition status. Depending on whether these territories are included, the total can rise above 195.
What Makes a Country a Country
To better understand how many countries are there in the world, it helps to know what qualifies as a country. Generally, a country must have sovereignty, meaning it governs itself without external control. It should also have recognized borders and the capacity to interact diplomatically with other nations.
However, recognition is political, not scientific. A country may meet all practical criteria but still be excluded from international organizations due to geopolitical conflicts. This reality explains why counting countries is not purely mathematical.
United Nations vs. Non-UN States
The United Nations recognizes 193 member states, which forms the core of the global count. Adding Vatican City and Palestine brings the number most people accept when answering how many countries are there in the world.
Vatican City is unique because it is governed by the Holy See and has a religious leadership structure. Palestine holds observer status and is recognized by many, but not all, UN members. These exceptions highlight how political agreement shapes international classification.
Countries, Territories, and Dependencies
Another source of confusion comes from territories and dependencies. Places like Puerto Rico, Greenland, and Hong Kong are often mistaken for countries. While they have distinct cultures and local governments, they are not sovereign states.
This distinction is essential when discussing how many countries are there in the world. Territories do not conduct independent foreign policy, which is a key feature of recognized countries.
Continents and Regional Distribution
Looking at how many countries are there in the world by continent provides additional insight. Africa has the highest number with 54 countries, followed by Asia and Europe. Oceania has the fewest due to its large oceanic geography and small population centers.
This distribution reflects colonial history, independence movements, and regional politics. Understanding these patterns helps explain why the global count looks the way it does today.
Historical Changes in Country Numbers
The answer to how many countries are there in the world has changed over time. In 1900, far fewer independent nations existed due to colonial rule. The mid-20th century saw a surge in new countries as colonies gained independence.
Political changes continue to reshape borders. New countries can emerge, and existing ones can merge or dissolve. This dynamic nature means the global count is not permanently fixed.
Why the Question Still Matters
Knowing how many countries are there in the world is more than trivia. It affects international law, global trade, travel, education, and diplomacy. Accurate understanding helps businesses expand internationally, students learn geography correctly, and governments maintain proper relations.
In an increasingly connected world, clarity about country status supports better global communication and cooperation.
Conclusion
So, how many countries are there in the world? The most accurate and widely accepted answer is 195, based on United Nations recognition and observer status. However, political realities mean that alternative counts exist depending on definitions and recognition criteria. Understanding the reasoning behind the numbers provides a deeper appreciation of global politics and international structure. The world map is not just a collection of borders but a living record of history, power, and identity.
Meta Description:
How many countries are there in the world? Learn the official number, why it varies, and how global recognition really works.
SEO Category: Informational